National Treaty Recognition Week, observed from November 5th to 11th, is an opportunity to delve into the significance and complexities of treaties, particularly within the context of Canada. This article aims to demystify the concept of treaties and explore the differences between the numbered treaties, which came into existence after 1791 and were registered in Canadian jurisdiction, and the Haldimand Treaty of 1779 and the subsequent Haldimand Proclamation of 1784. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in recognizing the unique status and implications of these agreements.
Numbered Treaties: Domestic Internal Agreements
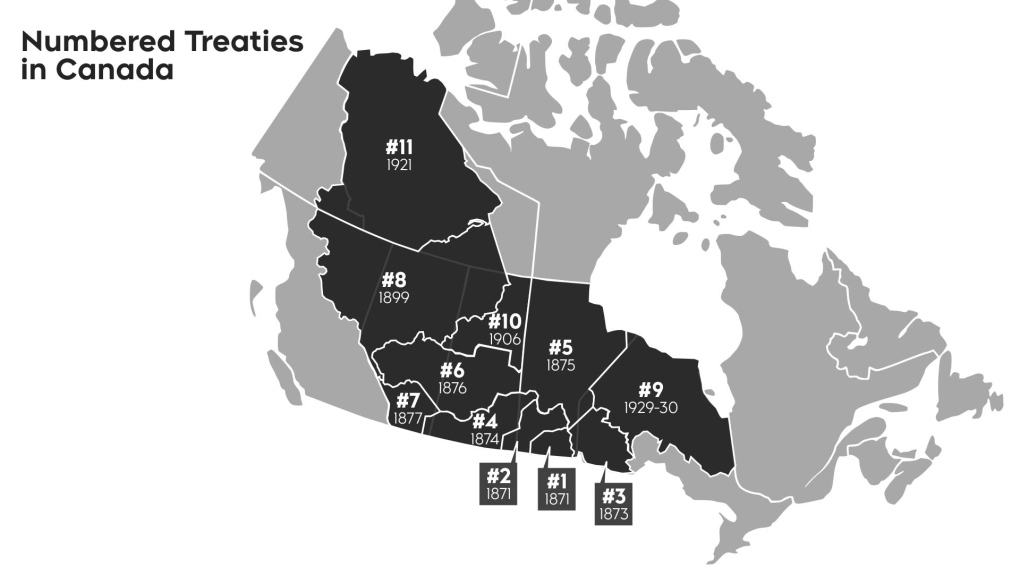
In Canada, a series of treaties known as the “Numbered Treaties” were established between the Canadian government and various Indigenous nations from 1871 onwards. These treaties primarily cover land rights, resource sharing, and other provisions aimed at fostering peaceful coexistence. The key distinction to note is that these treaties are considered internal agreements, designed to regulate relations within the newly-formed Canadian confederation.
As internal agreements, the Canadian government holds the authority to modify or change the provisions of the Numbered Treaties with the consent of the Indigenous nations involved. These treaties have been registered within the Canadian legal framework, allowing for adjustments as required over time.
The Haldimand Treaty of 1779 and Haldimand Proclamation of 1784: Imperial Instruments
In contrast to the Numbered Treaties, the Haldimand Treaty of 1779 and the accompanying Haldimand Proclamation of 1784 predate the formation of the Canadian confederation. These agreements were established by the British government and were part of its broader efforts to secure the loyalty and cooperation of Indigenous nations during the American Revolutionary War.
The Haldimand Treaty granted the Mohawk Nations of the Grand River Country a sizable tract of land adjacent to what is now southwestern Ontario. The Haldimand Proclamation further reaffirmed the promises made in the treaty, protecting the rights and interests of the Indigenous peoples in the territory.
As imperial instruments, these agreements are international in nature and not subject to alteration by the Canadian government alone. They represent commitments made by the British Crown and hold a unique status in the eyes of international law.
The distinction between the Canadian Numbered Treaties and the Haldimand Treaty and Proclamation lies in their historical origins and the nature of their agreements. Numbered Treaties are internal agreements, which Canada has the authority to modify as a direct party, while the Haldimand Treaty and Proclamation are imperial instruments and international treaties, beyond the scope of unilateral Canadian alteration.
Recognizing and respecting the unique status of these treaties is essential in fostering meaningful relationships with Indigenous nations and upholding the principles of reconciliation and justice in Canada. National Treaty Recognition Week provides an opportunity to deepen our understanding of these agreements and their ongoing significance.







